Overview
Machine Learning
Explicitly programmed:
power <- function(a,b) {
c <- a^b # known function
return(c)
}
power(1,3)
## 1
power(2,3)
## 8
power(3,4)
## 81
Machine Learning
What if we don’t know what function to apply, but we have a lot of examples?
func(2)
## 2.895133
func(1)
## 1.666248
func(6)
## 6.399109
Machine Learning
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
- Supervised machine learning algorithms
- Unsupervised machine learning algorithms
- Reinforcement machine learning algorithms
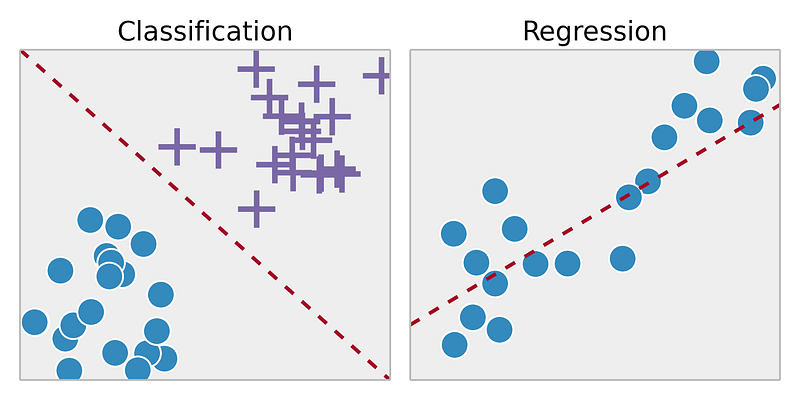
Supervised machine learning
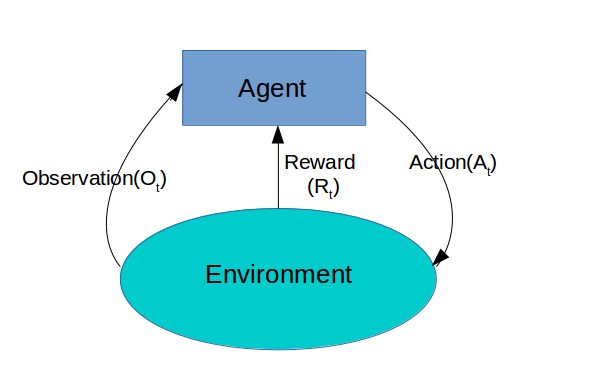
Unsupervised machine learning

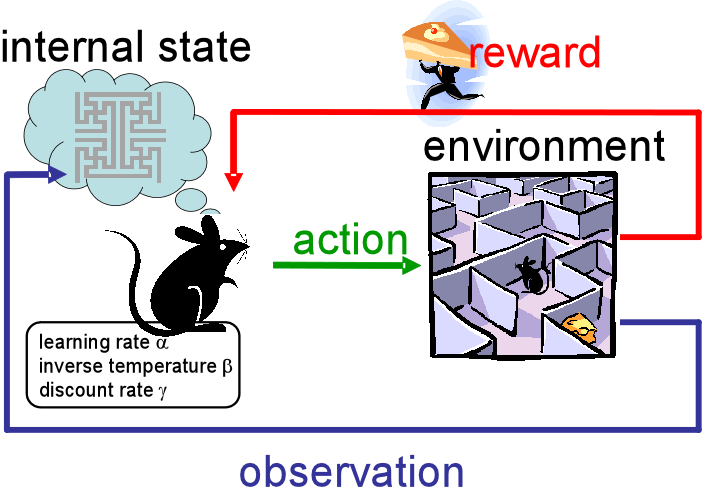
Reinforcement machine learning
Artificial Neural Network - ANN
Single-layer Perceptron
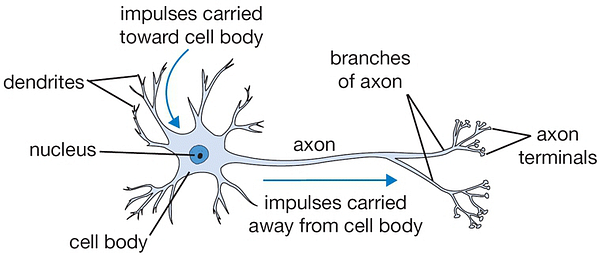
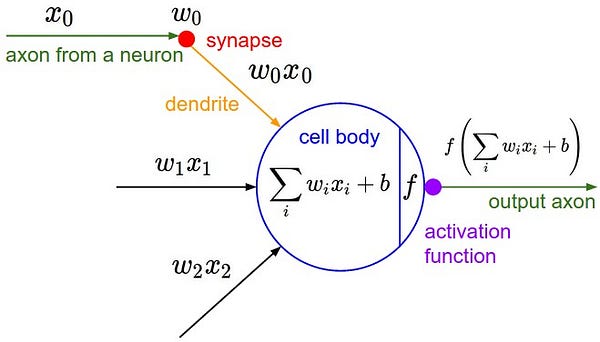
- Input Nodes (input layer)
- Connections and Weights
- Activation Function
- Output Nodes (output layer)
## ## Attaching package: 'matrixStats'
## The following object is masked from 'package:plyr': ## ## count
Artificial Neural Network - ANN
Single-layer Perceptron
Let’s try and predict rating:
| calories | protein | fat | sodium | fiber | rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 4 | 1 | 130 | 10.0 | 68 |
| 120 | 3 | 5 | 15 | 2.0 | 34 |
| 70 | 4 | 1 | 260 | 9.0 | 59 |
| 50 | 4 | 0 | 140 | 14.0 | 94 |
| 110 | 2 | 2 | 180 | 1.5 | 30 |
Artificial Neural Network - ANN
Single-layer Perceptron
Artificial Neural Network - ANN
Single-layer Perceptron
| calories | protein | fat | sodium | fiber | rating | pred_rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | 3 | 5 | 15 | 2.0 | 34 | 31 |
| 70 | 4 | 1 | 260 | 9.0 | 59 | 70 |
| 110 | 2 | 2 | 180 | 1.5 | 30 | 34 |
| 90 | 2 | 1 | 200 | 4.0 | 49 | 47 |
| 120 | 1 | 2 | 220 | 0.0 | 18 | 22 |
Artificial Neural Network - ANN
Deep Learning
Artificial Neural Network - ANN
Deep Learning
| calories | protein | fat | sodium | fiber | rating | pred_rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | 3 | 5 | 15 | 2.0 | 34 | 34 |
| 70 | 4 | 1 | 260 | 9.0 | 59 | 65 |
| 110 | 2 | 2 | 180 | 1.5 | 30 | 34 |
| 90 | 2 | 1 | 200 | 4.0 | 49 | 48 |
| 120 | 1 | 2 | 220 | 0.0 | 18 | 20 |
Deep Learning
Components:
Network has 1 Layer Input with 5 nodes and 1 Layer Output with 1 node.
Deep Learning
Components:
Network has 3 hidden layers.
Deep Learning
Components:
1st Layer: 20nodes
Deep Learning
Components:
2nd Layer: 15nodes
Deep Learning
Components:
3d Layer: 5nodes
Deep Learning
Components:
4th Layer: 1node
Deep Learning
Components:
Train it with Backpropagation (change weights)
Computer Vision - CV
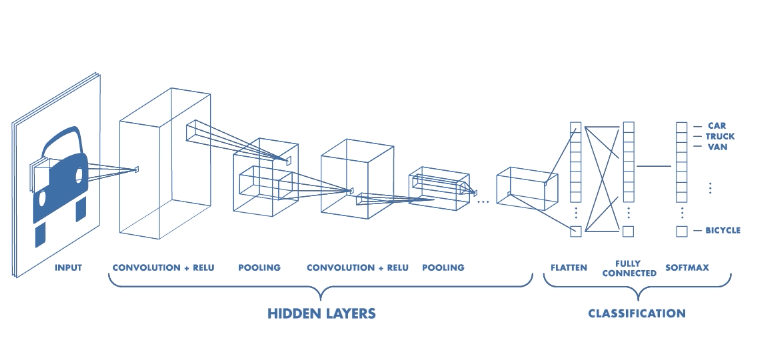
Computer Vision - CV

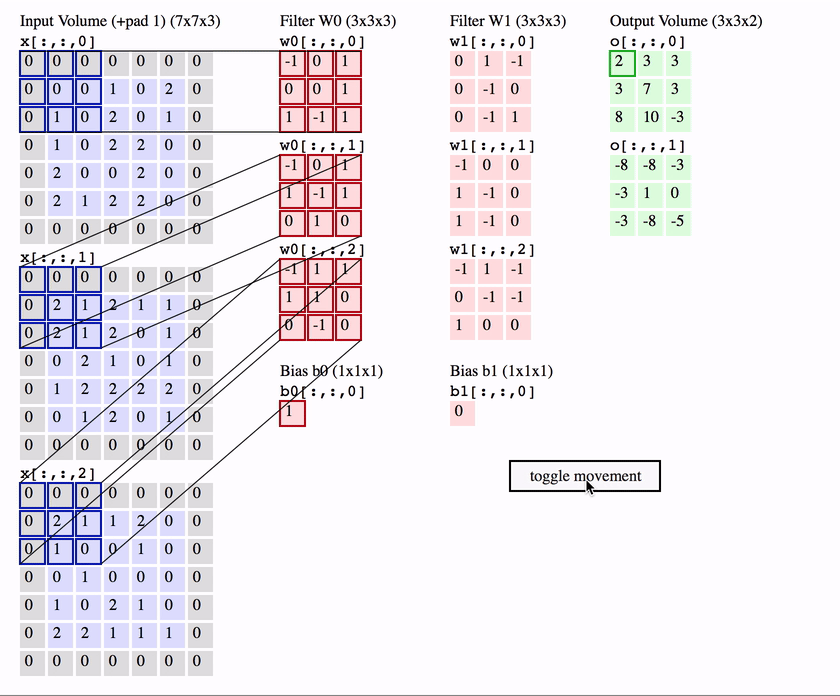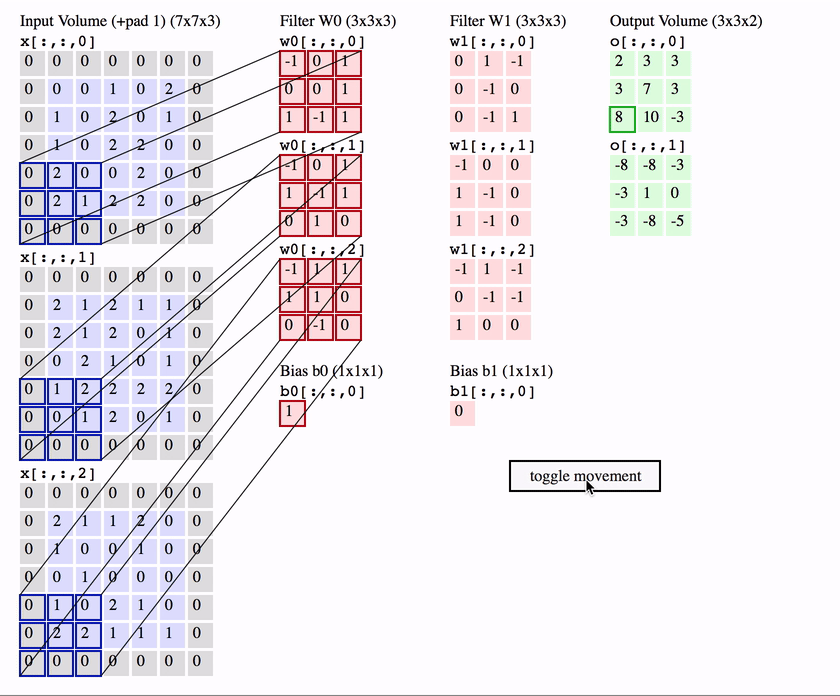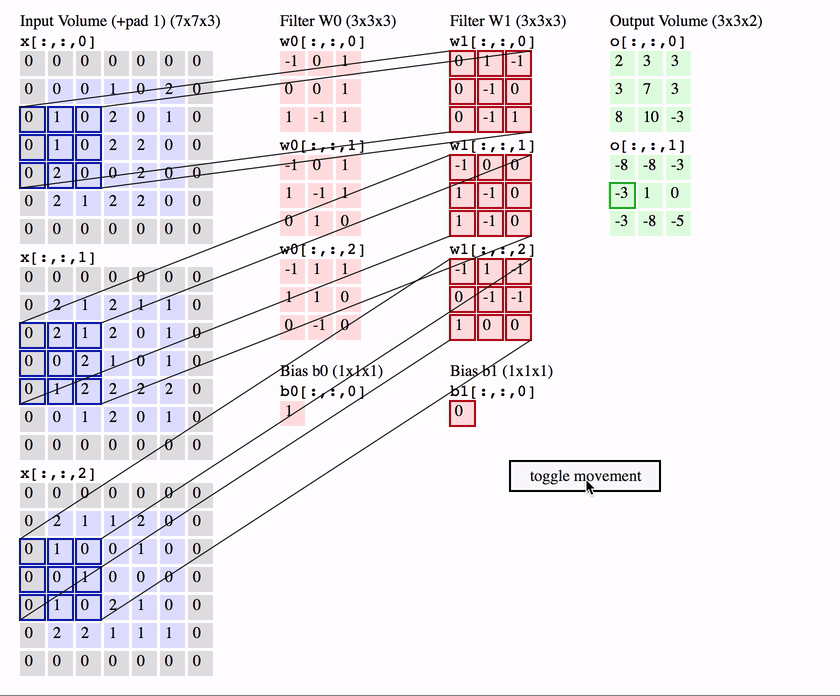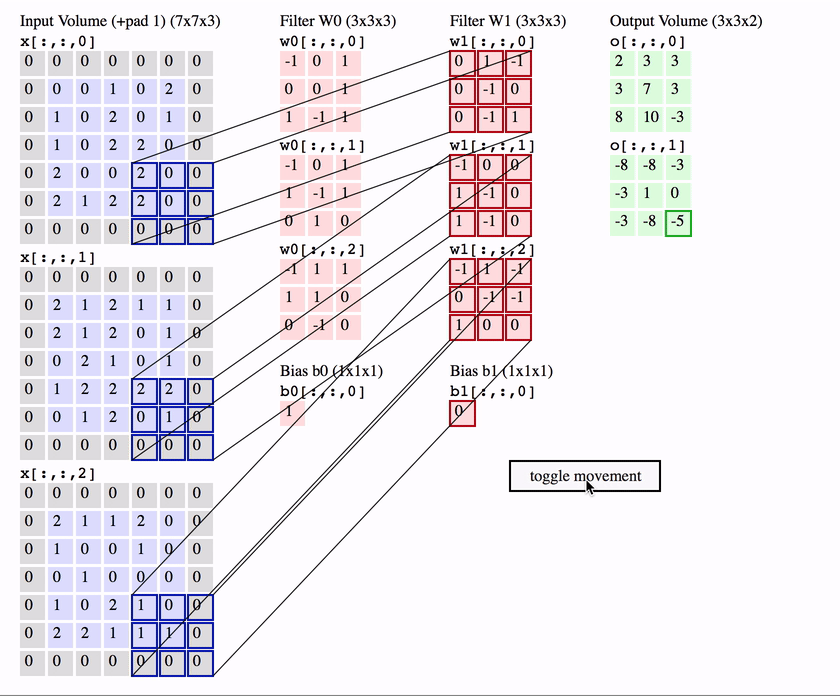
Computer Vision - CV
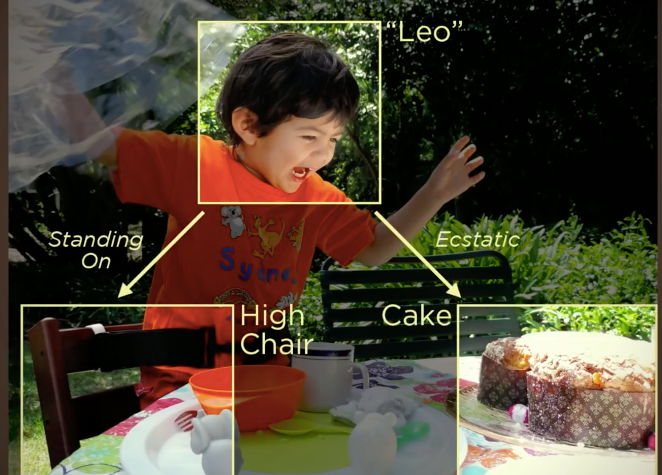
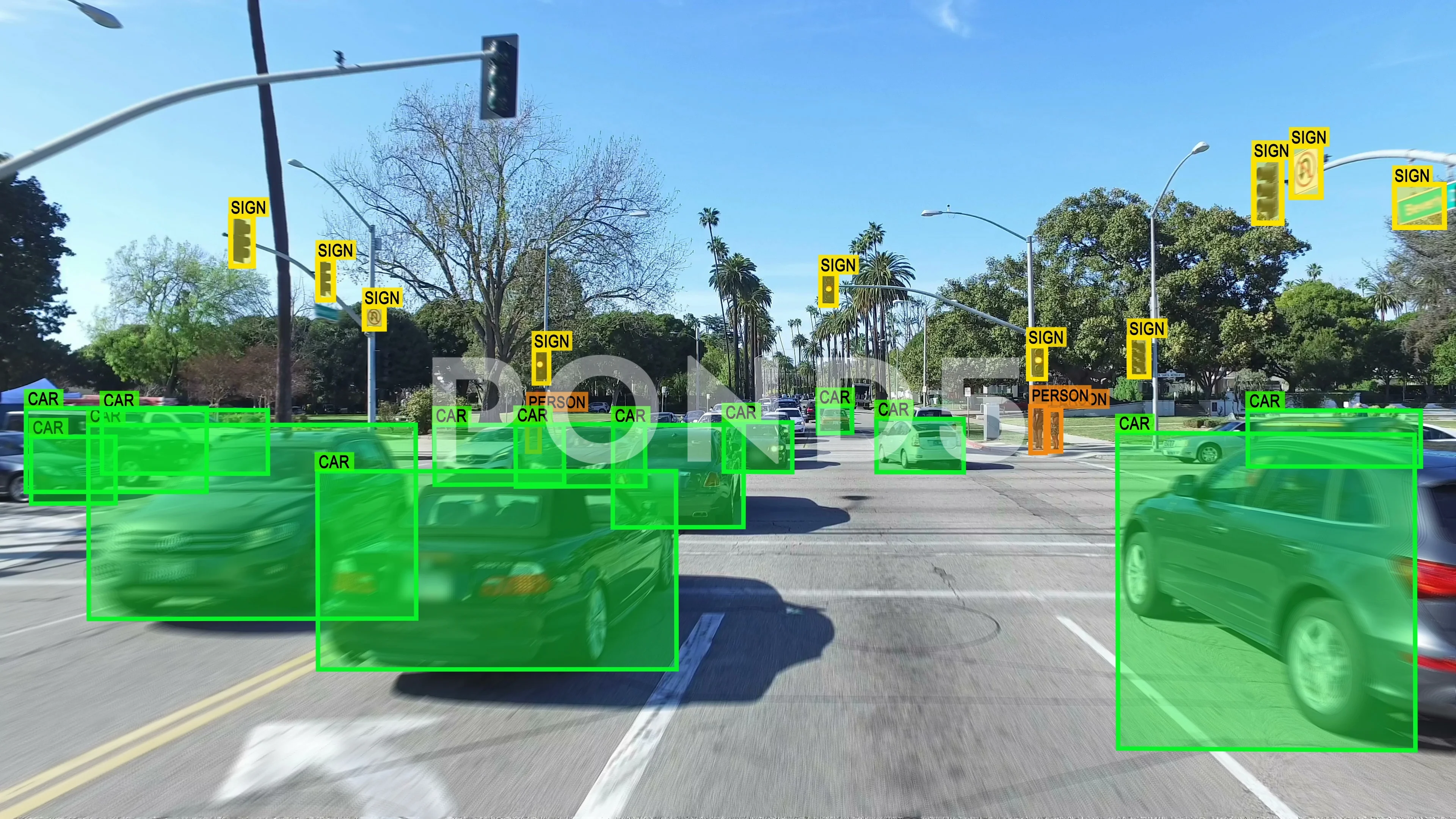

Natural Language Processing - NLP



Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings

Cats are mammals.
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
Cats are mammals.
w1 w2 w3
cats - are
are - cats
are - mammals
mammals - cats
cats - mammals
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
Keep values of middle network as embeddings for input word
cat = [0.8874 0.4184 0.9876 0.2662 0.0479 0.5825 0.3993 0.0556 0.1302 0.8568 0.4025 0.5344 0.9492 0.0258 0.7850 0.1779 0.4387 0.9506 0.2799 0.9741 0.4159 0.9542 0.9834 0.1766 0.1999 0.2395 0.8560 0.1893 0.5676 0.2971 0.4173 0.6742 0.6488 0.4010 0.5583 0.4708 0.1981 0.4244 0.7771 0.9306 0.0068 0.3926 0.1718 0.5491 0.2884 0.3237 0.8570 0.2799 0.4225 0.2305]
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
Keep values of middle network as embeddings for input word
cat = [0.8874 0.4184 0.9876 0.2662 0.0479 0.5825 0.3993 0.0556 0.1302 0.8568]
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
Keep values of middle network as embeddings for input word
cat = [0.8874 0.4184 0.9876 0.2662 0.0479 0.5825 0.3993 0.0556 0.1302 0.8568]
The Marvelous Mathematics of Computational Linguistics:
King - Man + Woman = Queen
Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
The Marvelous Mathematics of Computational Linguistics:
King - Man + Woman = Queen

Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings


Natural Language Processing - NLP
Word Embeddings
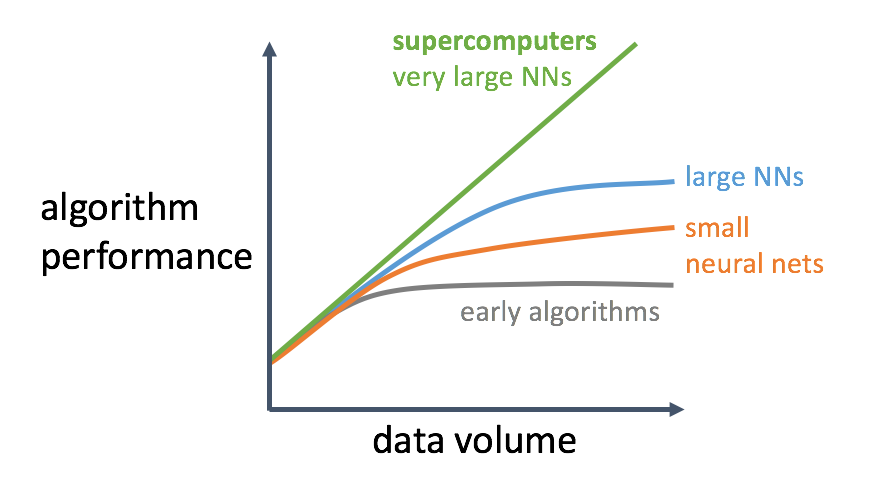
Why Big Data?
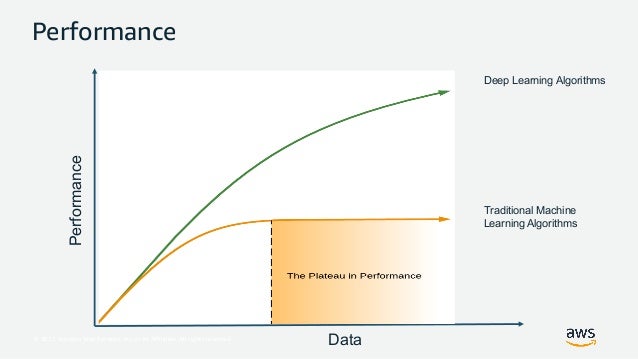
Why Big Data?
How much is Big Data?

Why Big Data?

Why Big Data?
Talon Supports Machine Learning








Talon Supports Machine Learning
Will add:


Talon Supports Machine Learning
Fast prototyping.
Machine Learning code templates.
Model Interpretation.
Big Data pipelines.
Workshops and tutorials.
Future Workshops & Tutorials?
Computer Vision.
Natural Language Processing.
Multi GPU training.
General Deep Learning.
Handle Big Data.
Quick Prototyping.
Other?
Thank you!
https://towardsdatascience.com/a-gentle-introduction-to-neural-networks-series-part-1-2b90b87795bc